
#Tibia and fibula fracture full
Full weight bearing can be done by weeks 2-4. This is best for low impact fractures that have minimal comminution and minimal displacement. If treated without surgery, the leg fractures are reduced and a long leg cast is applied with progressive weight bearing. These can be treated with or without surgery. The second is the Tscherne Classification system, which classifies the amount of soft tissue injury associated with closed fractures of the tibia and fibula. The first is the Gustilo and Anderson Classification, which classifies open fractures and degree of soft tissue injury. There ae two named classification systems.

The fracture may be transverse but there may be fracture lines that go up to the knee joint or down to the ankle joint. If there is a defect, it means that part of the bone has been lost. If there is a great deal of displacement, it means that a part of the bone may have lost its blood supply. The doctor must look for comminution of the fracture, commonly seen in high impact fractures. Post reduction films must be taken of these same areas to see if everything is aligned. The ankle and knee must be included in those x-rays because of a high incidence of secondary injuries to these areas. X-rays of the entire lower leg must be taken in both the front and side views. About five percent of all tibial fractures are broken in two places. If the tibial shaft is fractured, then there is a high incidence of knee ligamentous injuries. There are four compartments to be concerned about in these types of fractures. The lower leg must be evaluated for compartment injury. Soft tissue injury must be expected and evaluated. The dorsalis pedis artery and the posterior tibial artery pulses must be established, especially if the fracture is open. MRI testing may have to be done to show the presence of these injuries.Įvaluation of Tibia and Fibula Shaft FracturesĮvaluation of the nerves and blood vessels is vital to evaluating these injuries. Ballet dancers can get stress fractures as well. This can happen with military recruits who must stand and march all day long. Stress fractures can happen to these bones, especially the fibula. There is usually little injury to the soft tissue. The fall doesn’t have to be from a great height in order to cause a fracture. Indirect fractures of the tibia and fibula can occur with falls when the foot twists. These are often seen as spiral fractures with rotational injuries.
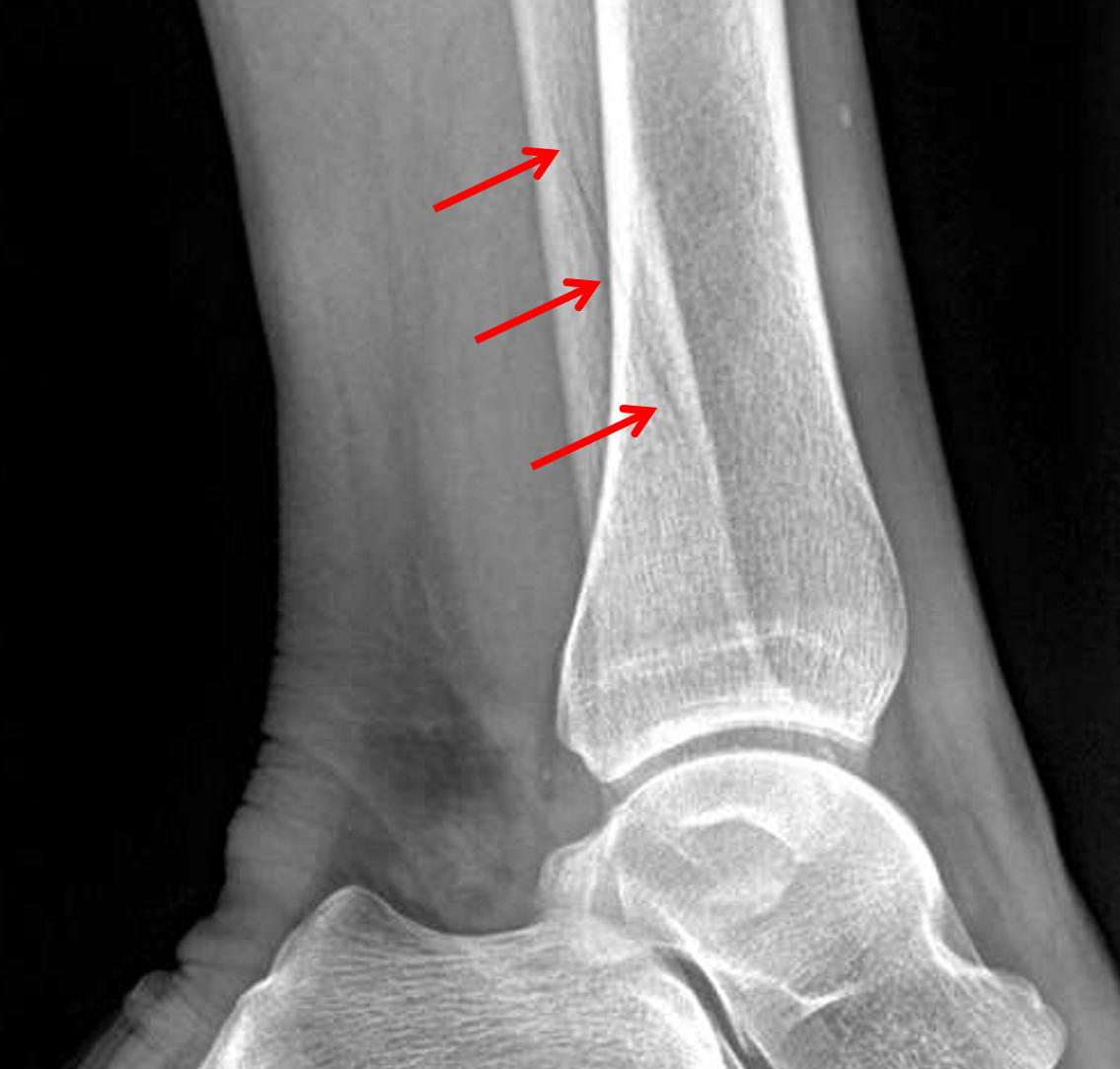
In fibular shaft fractures, direct trauma to the lateral leg is usually the cause. These can also be comminuted and can result in open fractures or compartment syndrome.

Low energy bending injuries can occur with oblique or transverse fractures or butterfly fragments. Compartment syndrome and open fractures can happen and must be looked out for.
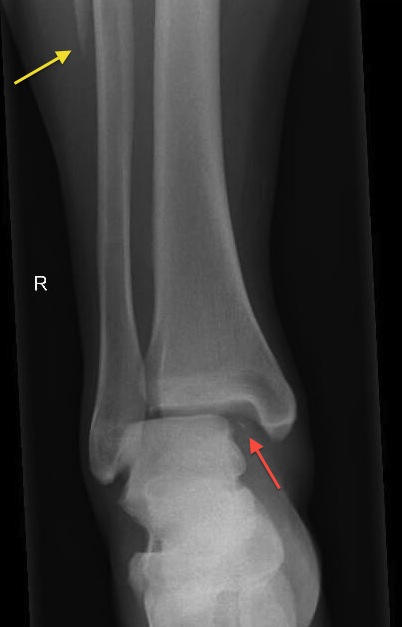
This results commonly in comminuted, transverse and displaced fractures with a great deal of soft tissue injuries. The main mechanism of injury in a tibia/fibula shaft fracture is a high energy bending injury, such as is seen in a motor vehicle accident. The common peroneal nerve runs alongside the neck of the fibula and so it is commonly injured when the fibula is injured. The fibula’s function is more for muscle insertion than it is for weight bearing. The fibula carries only about 6-17 percent of the total weight bearing capacity of the lower leg. The tibia is the bone that carries the bulk of a person’s weight. There is a relatively high rate of nonunion in these types of fractures. The average age of a tibial fracture is 37 years of age. There can also be fractures in 90-99 year old females at a rate of 49 out of 100,000 people in this age group. Most of these injuries occur in males aged 15-19 years. There are about 26 tibia/fibular fractures per 100,000 people. These represent the most common long bone fractures. I’m Ed Smith, a Sacramento Auto Accident Lawyer. Fractures of the tibia and fibula involve the two long bones of the lower leg.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
